Difference between revisions of "Seat Availability Parameters"
| (2 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
*[[Inventory Screen]] | *[[Inventory Screen]] | ||
*[[Operational Flight Inventory Management]] | *[[Operational Flight Inventory Management]] | ||
| − | *[[Business Rules | + | *[[Business Rules for Inventory Management]] |
*[[Mass Operations]] | *[[Mass Operations]] | ||
*[[Special Spaces Management]] | *[[Special Spaces Management]] | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
*[[Commercial Agreements Management]] | *[[Commercial Agreements Management]] | ||
*[[System Queue Management]] | *[[System Queue Management]] | ||
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Reports]] |
*[[Dictionaries]] | *[[Dictionaries]] | ||
*[[User Rights and Roles]] | *[[User Rights and Roles]] | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
*[[Charter Flight Creation]] | *[[Charter Flight Creation]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Inventory]] |
Latest revision as of 14:10, 2 September 2021
About Seat Availability
Seat availability (the AV parameter) is calculated for cabin booking class on a segment as the difference between a value of sale capacity in a booking class taking into account overbooking (the AU parameter) and a number of seats booked for the given period (the Bkd parameter).
When segment capacity parameters or a number of booked seats is changed, recalculation of the seat availability parameter for all the mentioned booking classes, cabins, segments and legs is carried out.
Seat Availability Calculation Algorithms
There are three algorithms of calculation of seats availability:
- Top Down: booked seats in a booking class are subtracted from the quota of this class and when the quota is exceeded, the seats are subtracted from the quota of the next subordinate class in the structure which contains vacant seats.
- Bottom Up: booked seats in a booking class are subtracted from the quota of this class and when the quota is exceeded, the seats are subtracted from the quota of the lowest class in the structure which contains vacant seats.
- Up Sell: booked seats in a booking class are subtracted from the quota of the lowest class in the structure which contains vacant seats.
Seat availability calculation algorithm on a route segment of a flight is set by the "AV Calculation" business rule.
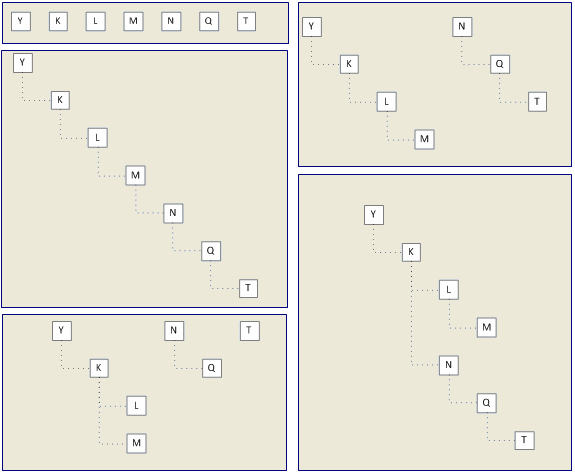
RBD Interrelation (Nesting)
Structure of RBD interrelation (nesting) affects calculation of values of seat availability in booking classes. When calculating values of seat availability (taking into account nesting), a number of seats available in classes which are subordinate in the nesting structure is also available for booking in higher classes.
A class which contains subordinate classes is called the parental class. A class which is subordinate to parental class is called the affiliated class.
Nesting structure is defined by the "Nesting" business rule.
Examples of nesting structure are presented in the figure.
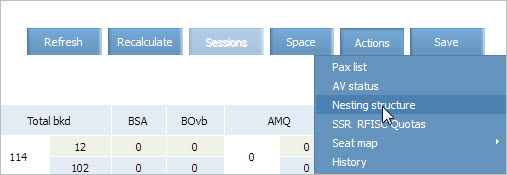
You may view the nesting structure on the inventory screen by clicking Actions → Nesting structure.
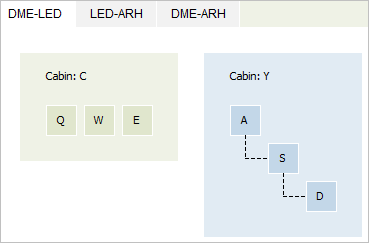
This report presents graphic view of the nesting structure defined by the "Nesting" business rule
The report contains data for each segment. By default, nesting structure on the first segment is presented. To view information on other segment, click on a tab with its name.
See also:
- Inventory Screen
- Operational Flight Inventory Management
- Business Rules for Inventory Management
- Mass Operations
- Special Spaces Management
- Flight Reports
- Ancillaries Settings
- Publishing Flight Inventory Data to External Systems
- PFS Data Management